To
understand TCP/IP Model you need to understand some basics.
Protocol - A protocol is a set of rules that govern how systems
communicate. For networking they govern how data is transferred from one system to another.
Protocol Suite - A
protocol suite is a collection of protocols that are designed to work together.
Protocol Stacks - It is possible to write a single
protocol that takes data from one computer application and sends it
to an application on another computer.- A Single stack Protocol
The problem with
this approach is that it very inflexible, as any changes require changing the
entire application and protocol software.
The approach used
in networking is to create layered protocol stacks.
Each level of the
stack performs a particular function and communicates with the
levels above and below it.
This layered
arrangement is not confined to networking, and how it works is probably best
understood if you compare it to real life example.
Lets take an
example of a parcel service between two offices.
The task is simple
– send parcels between people in each office.
We will divide the
task into two distinct processes as follows:
1 Take a package, wrap it and
address it.
2 Send it to the destination
At the receiving
end
1 Receive the package
2 Deliver it to the
recipient
Typically you would have
an internal mail man that:
Collects the parcels
from the senders and takes then to a mail dispatch room.
The parcels are placed
in a van by the dispatcher and then driven to the remote office.
At the remote
office
1 The parcels are received by
the dispatcher and placed into a tray for the mail man
2.The mail man collects the parcels
and delivers them to the recipients.
The question really
is what is the advantage of splitting the task into different layers/tasks?
The answer is that
any of the layers/tasks can be changed without affecting the other layers.
So if for example,
if we decide to use a train instead of a van to transport the messages between
the offices we could do so without affecting the mail man.
In fact the mail
man doesn’t know, and doesn’t care, how the parcels are transported between the
offices, as all he does is collect them, and pass them to the delivery man.
Although this
appears very simple, and maybe trivial, it does illustrate some very important
points that are crucial when it comes to understanding networking
protocols and how they are organised.
Layer 1, the physical layer, defines electrical aspects of
activating and maintaining physical links in networks. The physical layer
represents the basic network hardware, such as switches and routers.
Layer 2, the Data link layer, provides a
reliable synchronization and transfer of information across the physical layer
for accessing the transmission medium. Layer 2 specifies how packets access
links and are attached to additional headers to form frames when entering a new
networking environment, such as a LAN. Layer 2 also provides error detection
and flow control.
Layer 3, the network layer (IP) specifies the
networking aspects. This layer handles the way that addresses are assigned to
packets and the way that packets are supposed to be forwarded from one end
point to another.
Layer 4, the transport layer, lies just above the network
layer and handles the details of data transmission. Layer 4 is implemented in
the end-points but not in network routers and acts as an interface protocol
between a communicating host and a network. Consequently, this layer provides
logical communication between processes running on different hosts.
Layer 5, the application layer, determines how a specific
user application should use a network. Among such applications are the Simple
Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP),
and the World Wide Web (WWW).
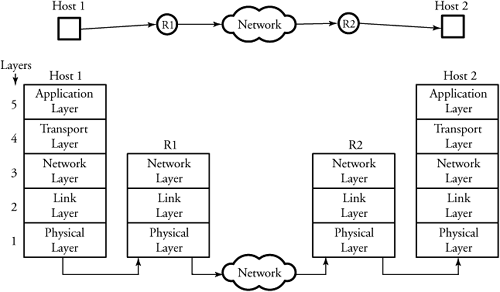
.
The transmission of a given message between two users is carried out by
(1) flowing down the data through each and all layers of the transmitting end,
(2) sending it to certain layers of protocols in the devices between two end
points, and (3) when the message arrives at the other end, letting the data
flow up through the layers of the receiving end until it reaches its
destination. A message is transmitted from host 1 to host 2, and, all five
layers of the protocol model participate in making this connection. The data
being transmitted from host 1 is passed down through all five layers to reach
router R1. Router R1 is located as a gateway to the operating regions of host 1
and therefore does not involve any tasks in layers 4 and 5. The same scenario
is applied at the other end: router R2. Similarly, router R2, acting as a
gateway to the operating regions of host 2, does not involve any tasks in
layers 4 and 5. Finally at host 2, the data is transmitted upward from the
physical layer to the application layer.
The main idea of the
communication protocol stack is that the process of communication between two
end points in a network can be partitioned into layers, with each layer adding
its own set of special related functions. a different way of realizing protocol
layers used for two hosts communicating through two routers. This figure
illustrates a structural perspective of a communication set-up and identifies
the order of fundamental protocol layers involved

Comments
Post a Comment